Attributes
The ATTRIBUTE-ID syntax allows for the definition of new attribute types, which can be used in various contexts (see attribute-clause).
Context:
Program Structure Types
attribute-specification

attribute-header
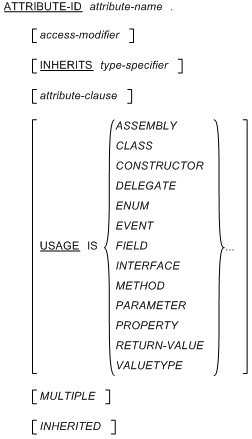
Example
Note that, when compiling for JVM COBOL, instance members (that is, constructors, methods or properties) are ignored, but do not cause a compilation error. Similarly, the keyword PROPERTY on fields is also ignored in this case.
An example of a simple attribute, which can be used interchangeably both on .NET and on JVM COBOL is:
attribute-id AuthorAttribute.
01 #value string.
method-id new(auth as string).
set #value to auth
end method.
end attribute.On .NET, the resulting code is equivalent to the following .NET COBOL class:
class-id AuthorAttribute inherits type System.Attribute
01 #value string.
method-id new(auth as string).
set #value to auth
end method.
end class.On JVM, the resulting code is equivalent to the following Java annotation:
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AuthorAttribute
{
public String value();
}