This section focuses on the other facilities available for managing transactions. It includes information on using the VisiTransact Transaction Service interfaces—TransactionFactory, Control, Coordinator, and Terminator.
Although typically you will use the Current interface to manage transactions, there are several other approaches to transaction management you can use:
|
•
|
Indirect Context Management with Explicit Propagation. The client uses a combination of the Current, Control, and other objects which describe the state of the transaction. A client application that uses the Current object (and therefore, is also automatically using implicit propagation) can use explicit propagation by gaining access to the Control object with the Current::getControl() method. It can use a VisiTransact Transaction Service object as an explicit parameter to a transactional object. This is explicit propagation.
|
|
•
|
Direct Context Management with Implicit Propagation. The client uses a combination of the Current, Control, and other objects which describe the state of the transaction. A client that accesses the VisiTransact Transaction Service objects directly can use the Current::resume() method to set the implicit transaction context associated with its thread. This allows the client to invoke methods of objects that require implicit propagation of the transaction context.
|
|
•
|
Direct Context Management with Explicit Propagation. The client application directly accesses the Control object and the other objects which describe the state of the transaction. To propagate the transaction to an object, the client must include the appropriate VisiTransact Transaction Service object as an explicit parameter of a method.
|
|
•
|
TransactionFactory. This interface defines methods that allow a transaction originator to begin a transaction. To view the TransactionFactory interface, see “Creating transactions with the TransactionFactory”.
|
|
•
|
Control. This interface allows an application to explicitly manage or propagate a transaction context. To view the Control interface, see “Gaining control of a transaction with the control object”.
|
|
•
|
Terminator. This interface enables an application to commit or rollback transactions. Typically, its methods are used by transaction originators—however, by propagating the Control or Terminator object, any transaction participant can commit or rollback the transaction. To view the Terminator interface, see “Committing or rolling back transactions with Terminator”.
|
|
•
|
Coordinator. This interface enables a participant to determine the status of a transaction, discover the transaction name, obtain the transaction context, as well as designate that a transaction should be rolled back from a participant other than the transaction originator. See “Marking a transaction for rollback” and “Obtaining transaction information” for information on methods in the Coordinator interface.
|
The TransactionFactory interface is provided to allow the transaction originator to begin a transaction. As shown in the following example, this CosTransactions interface provides two methods—create() and recreate(). The create() method is used to start a new transaction. The recreate() method is used to create a transaction's Control object from a propagation context and is not typically used by a normal application.
module CosTransactions
{
interface TransactionFactory
{
Control create(in unsigned long time_out);
Control recreate(in PropagationContext ctx);
};
};
{
interface TransactionFactory
{
Control create(in unsigned long time_out);
Control recreate(in PropagationContext ctx);
};
};
VisiTransact also supplies an extension to the TransactionFactory interface that allows a transaction to be created using a specific name—create_with_name(). Naming a transaction is useful for tracking the progress of a particular transaction, as well as debugging its execution.
module VISTransactions
{
// TransactionFactory
// This extends the CosTransactions::TransactionFactory by
// allowing someone to create a transaction with a user-defined
// name that can be used for debugging, error reporting, etc.
interface TransactionFactory : CosTransactions::TransactionFactory
{
CosTransactions::Control create_with_name(in unsigned long time_out,
in string userTransactionName);
};
};
{
// TransactionFactory
// This extends the CosTransactions::TransactionFactory by
// allowing someone to create a transaction with a user-defined
// name that can be used for debugging, error reporting, etc.
interface TransactionFactory : CosTransactions::TransactionFactory
{
CosTransactions::Control create_with_name(in unsigned long time_out,
in string userTransactionName);
};
};
The following table defines the methods for creating transactions with TransactionFactory.
|
Creates a new transaction and returns a Control object which can be used to manage participation in the new transaction. If time_out is set to 0 seconds, the default timeout for the instance of the VisiTransact Transaction Service is used.
|
|
|
Creates a new transaction with a user-defined name as supplied in the userTransactionName argument.
|
|
|
Creates a new representation of an existing transaction as defined by the PropagationContext (the transaction context) and returns a Control object. The Control object can be used to manage or control participation in the existing transaction.
|
For more information about the TransactionFactory interface, see TransactionFactory interface in the VisiBroker for C++ API Reference.
...
CosTransactions::TransactionFactory_var txnFactory;
CosTransactions::Control_var control;
control = txnFactory->create_with_name
(0,"BankTransfer#1");
//use default
//timeout value
...
CosTransactions::TransactionFactory_var txnFactory;
CosTransactions::Control_var control;
control = txnFactory->create_with_name
(0,"BankTransfer#1");
//use default
//timeout value
...
The PropagationContext can be obtained from an existing transaction using the CosTransactions:Coordinator::get_txcontext() method described in “Obtaining transaction information”.
The Control interface allows an application to obtain the Terminator and Coordinator object references in order to explicitly manage or propagate a transaction context. An object supporting the Control interface is associated with one specific transaction.
The following example shows the Control interface.
module CosTransactions
{
interface Control
{
Terminator get_terminator()
raises(Unavailable);
Coordinator get_coordinator()
raises(Unavailable);
};
};
{
interface Control
{
Terminator get_terminator()
raises(Unavailable);
Coordinator get_coordinator()
raises(Unavailable);
};
};
The table below defines the methods for the Control interface.
|
Returns a Terminator object which supports operations to end the transaction. The Terminator object can be used to rollback or commit the transaction associated with the Control object. The CosTransactions::Unavailable exception is raised if the Control object cannot provide the Terminator object.
|
|
|
Returns a Coordinator object which supports operations needed by Resources to participate in a transaction. The Coordinator object can be used to register Resources for the transaction associated with the Control object. The CosTransactions::Unavailable exception is raised if the Control object cannot provide the Coordinator object.
|
...
CosTransactions::Control_var control
CosTransactions::Terminator_var newTranTerminator;
CosTransactions::Coordinator_var newTranCoordinator;
newTranTerminator = control->get_terminator();
newTranCoordinator = control->get_coordinator();
...
CosTransactions::Control_var control
CosTransactions::Terminator_var newTranTerminator;
CosTransactions::Coordinator_var newTranCoordinator;
newTranTerminator = control->get_terminator();
newTranCoordinator = control->get_coordinator();
...
With transactions originated using the TransactionFactory, the transaction originator handles transactions using several VisiTransact Transaction Service interfaces. Through these interfaces, more than one transaction may be managed at a time by the transaction originator.
With transactions originated using the TransactionFactory, you can use implicit propagation. See “Changing from explicit propagation to implicit”.
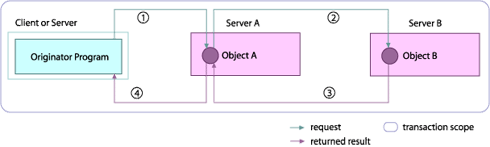
|
1
|
The transaction originator requests that Object A performs the doWork() method, passing a Control object or Coordinator object.
|
|
2
|
Object A requests that Object B performs the doMoreWork() method, and also passes it the Control or Coordinator object, allowing Object B to operate as part of the existing transaction.
|
The example below shows the Control object, control, being passed as an explicit parameter to the withdraw() method of the remote transactional object.
...
CosTransactions::Control_var control;
CORBA:Boolean didSucceed;
didSucceed=bank->withdraw(10, 444, control) // invoke a CORBA request
...
CosTransactions::Control_var control;
CORBA:Boolean didSucceed;
didSucceed=bank->withdraw(10, 444, control) // invoke a CORBA request
...
You may want to start a transaction with explicit propagation and then switch to implicit. To set up your implicit transaction context, pass the Control object into Current::resume(). See “Using multiple transactions within a context or thread” for details on using Current::resume() and Current::suspend().
If you start a transaction with implicit propagation and later want to get the transaction context explicitly, use Current::get_control().
The Terminator interface supports operations to commit or rollback a transaction. Typically, these operations are used by the transaction originator. The following example shows the Terminator interface.
module CosTransactions
{
interface Terminator
{
void commit(in boolean report_heuristics)
raises (HeuristicMixed, HeuristicHazard);
void rollback();
};
};
{
interface Terminator
{
void commit(in boolean report_heuristics)
raises (HeuristicMixed, HeuristicHazard);
void rollback();
};
};
The following table defines the methods provided by the Terminator interface.
|
Commits the transaction if the transaction has not been marked as rollback only, and if all of the participants in the transaction agree to commit. Otherwise, the transaction is rolled back and the CORBA::TRANSACTION_ROLLEDBACK exception is raised. When the transaction is committed, all changes to recoverable objects made in the scope of the transaction are made permanent and visible to other transactions or clients.
If the report_heuristics parameter is true, the VisiTransact Transaction Service will report inconsistent outcomes using the CosTransactions::HeuristicMixed and CosTransactions::HeuristicHazard exceptions.
|
|
The next example shows the MyBank interface for the transactional object which the originator is accessing to perform actions.
The following example shows how an originator either commits or rolls back a transaction involving the MyBank transactional object. This example is specific for working with transactions in the withdraw() method. Note that the balance() method would not be allowed to terminate the transaction since it is only passed the Coordinator.
...
CORBA::Boolean didSucceed;
...
CosTransactions::Terminator_var
txnTerminator=control->get_terminator();
if(didSucceed)
{ // invoke a CORBA request
try
{
txnTerminator->commit(1);
}
catch(CORBA::TRANSACTION_ROLLEDBACK&)
{
// Return failure.
}
}
else
{
txnTerminator->rollback();
}
...
CORBA::Boolean didSucceed;
...
CosTransactions::Terminator_var
txnTerminator=control->get_terminator();
if(didSucceed)
{ // invoke a CORBA request
try
{
txnTerminator->commit(1);
}
catch(CORBA::TRANSACTION_ROLLEDBACK&)
{
// Return failure.
}
}
else
{
txnTerminator->rollback();
}
...
See “Heuristic completion” for details about heuristic completion when committing a transaction.
If the participant does not want the transaction to commit, it can use the rollback_only() method from the Coordinator interface. When the rollback_only() method is called by a participant, the transaction associated with the current thread is modified so that the only possible outcome is to rollback the transaction. The CosTransactions::Inactive exception is raised if the transaction has already been prepared. The example below shows how a participant would use the rollback_only() method.
...
CosTransactions::Coordinator_var coord;
coord->rollback_only();
...
CosTransactions::Coordinator_var coord;
coord->rollback_only();
...
A participant can obtain information about a transaction such as the transaction name or transaction status, or obtain the transaction context for a transaction using methods in the Coordinator interface. The following table describes these methods.
|
Returns a PropagationContext object.
|
The get_status() method can return one of the following values: