 The RECORD clause specifies either the number of character positions in a fixed-length record or the range of character positions in a variable-length record. If the number of character positions varies, the clause specifies the minimum and maximum number of character positions.
The RECORD clause specifies either the number of character positions in a fixed-length record or the range of character positions in a variable-length record. If the number of character positions varies, the clause specifies the minimum and maximum number of character positions.
 The concepts of fixed and variable format files used throughout this section do not directly apply to line sequential files. See your COBOL system documentation on file handling for details on the implications of using line sequential files in your COBOL implementation.
The concepts of fixed and variable format files used throughout this section do not directly apply to line sequential files. See your COBOL system documentation on file handling for details on the implications of using line sequential files in your COBOL implementation.
 Although it is a part of the standard COBOL definition, the RECORD CONTAINS clause is explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
Although it is a part of the standard COBOL definition, the RECORD CONTAINS clause is explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
General Formats for Format 1
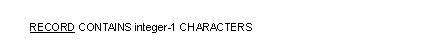

General Formats for Format 2
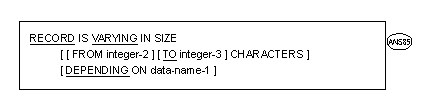
General Formats for Format 3

Syntax Rules for Format 1
- No record description entry for the file can specify a number of character positions different from integer-1.

Syntax Rules for Format 2
 Record descriptions for the file must not describe records which contain fewer character positions than specified by integer-2, nor records which contain a greater number of character positions than that specified by integer-3.
Record descriptions for the file must not describe records which contain fewer character positions than specified by integer-2, nor records which contain a greater number of character positions than that specified by integer-3.  Integer-3 must be greater than integer-2.
Integer-3 must be greater than integer-2.  Data-name-1 must describe an elementary unsigned integer in the Working-Storage or Linkage Section.
Data-name-1 must describe an elementary unsigned integer in the Working-Storage or Linkage Section.
General Rules for All Formats
- If the RECORD clause is not specified, the size of each data record is completely defined in the record description entry.
 If the associated file connector is an external file connector, all file description entries in the run unit which are associated with that file connector must specify the same values for integer-1 or integer-2 and integer-3. If the RECORD clause is not specified, all record description entries associated with this file connector must be the same length.
If the associated file connector is an external file connector, all file description entries in the run unit which are associated with that file connector must specify the same values for integer-1 or integer-2 and integer-3. If the RECORD clause is not specified, all record description entries associated with this file connector must be the same length. 
 Line sequential files are neither truly fixed nor truly variable format files: the presence or absence of any RECORDING MODE, RECORD CONTAINS or RECORD VARYING IN SIZE clause does not, therefore, impact their performance.
Line sequential files are neither truly fixed nor truly variable format files: the presence or absence of any RECORDING MODE, RECORD CONTAINS or RECORD VARYING IN SIZE clause does not, therefore, impact their performance.
General Rules for Format1
- Format 1 is used to specify fixed-length records. Integer-1 specifies the number of character positions contained in each record in the file.

General Rules for Format2
 Format 2 is used to specify variable-length records. Integer-2 specifies the minimum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file. Integer-3 specifies the maximum number of character positions in any record of the file.
Format 2 is used to specify variable-length records. Integer-2 specifies the minimum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file. Integer-3 specifies the maximum number of character positions in any record of the file.  The number of character positions associated with a record description is determined by the sum of the number of character positions in all elementary data items excluding redefinitions and renamings, plus any implicit FILLER items due to synchronization. If a table is specified:
The number of character positions associated with a record description is determined by the sum of the number of character positions in all elementary data items excluding redefinitions and renamings, plus any implicit FILLER items due to synchronization. If a table is specified:
- The minimum number of table elements described in the record is used in the summation above to determine the minimum number of character positions associated with the record description.
- The maximum number of table elements described in the record is used in the summation above to determine the maximum number of character positions associated with the record description.
 If integer-2 is not specified, the minimum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file is equal to the least number of character positions described for a record in that file.
If integer-2 is not specified, the minimum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file is equal to the least number of character positions described for a record in that file.  If integer-3 is not specified, the maximum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file is equal to the greatest number of character positions described for a record in that file.
If integer-3 is not specified, the maximum number of character positions to be contained in any record of the file is equal to the greatest number of character positions described for a record in that file.  If data-name-1 is specified, the number of character positions in the record must be placed into the data item referenced by data-name-1 before any RELEASE, REWRITE, or WRITE statement is executed for the file.
If data-name-1 is specified, the number of character positions in the record must be placed into the data item referenced by data-name-1 before any RELEASE, REWRITE, or WRITE statement is executed for the file.  If data-name-1 is specified, the execution of a DELETE, RELEASE, REWRITE, START, or WRITE statement or the unsuccessful execution of a READ or RETURN statement does not alter the content of the data item referenced by data-name-1.
If data-name-1 is specified, the execution of a DELETE, RELEASE, REWRITE, START, or WRITE statement or the unsuccessful execution of a READ or RETURN statement does not alter the content of the data item referenced by data-name-1.  During the execution of a RELEASE, REWRITE, or WRITE statement, the number of character positions in the record is determined by the following conditions:
During the execution of a RELEASE, REWRITE, or WRITE statement, the number of character positions in the record is determined by the following conditions:
- If data-name-1 is specified, by the content of the data item referenced by data-name-1.
- If data-name-1 is not specified and the record does not contain a variable occurrence data item, by the number of character positions in the record.
- If data-name-1 is not specified and the record does contain a variable occurrence data item, by the sum of the fixed portion and that portion of the table described by the number of occurrences at the time of execution of the output statement.
If the number of character positions in the logical record which is to be written is less than integer-2 or greater than integer-3, the output statement is unsuccessful and, except during execution of a RELEASE statement, the associated I/O status is set to a value indicating the cause of the condition.
 If data-name-1 is specified, after the successful execution of a READ or RETURN statement for the file, the contents of the data item referenced by data-name-1 indicates the number of character positions in the record just read.
If data-name-1 is specified, after the successful execution of a READ or RETURN statement for the file, the contents of the data item referenced by data-name-1 indicates the number of character positions in the record just read.  If the INTO phrase is specified in the READ or RETURN statement, the number of character positions in the current record that participate as the sending data items in the implicit MOVE statement is determined by the following conditions:
If the INTO phrase is specified in the READ or RETURN statement, the number of character positions in the current record that participate as the sending data items in the implicit MOVE statement is determined by the following conditions:
- If data-name-1 is specified, by the content of the data item referenced by data-name-1.
- If data-name-1 is not specified, by the value that would have been moved into the data item referenced by data-name-1 had data-name-1 been specified.
General Rules for Format 3
- When format 3 of the RECORD clause is used, integer-4 and integer-5 refer to the minimum number of characters in the smallest size data record and the maximum number of characters in the largest size data record respectively. However, in this case, the size of each data record is completely defined in the record description entry.
- The size of each data record is specified in terms of the number of character positions required to store the logical record, regardless of the types of characters used to represent the items within the logical record. The size of a record is determined by the sum of the number of characters in all fixed-length elementary items plus the sum of the maximum number of characters in any variable-length item subordinate to the record. This sum can be different from the actual size of the record. See the topic Selection Of Character Representation And Radix in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL Language, and the sections The SYNCHRONIZED Clause and The USAGE Clause.






![]() The RECORD clause specifies either the number of character positions in a fixed-length record or the range of character positions in a variable-length record. If the number of character positions varies, the clause specifies the minimum and maximum number of character positions.
The RECORD clause specifies either the number of character positions in a fixed-length record or the range of character positions in a variable-length record. If the number of character positions varies, the clause specifies the minimum and maximum number of character positions. ![]() The concepts of fixed and variable format files used throughout this section do not directly apply to line sequential files. See your COBOL system documentation on file handling for details on the implications of using line sequential files in your COBOL implementation.
The concepts of fixed and variable format files used throughout this section do not directly apply to line sequential files. See your COBOL system documentation on file handling for details on the implications of using line sequential files in your COBOL implementation. ![]() Although it is a part of the standard COBOL definition, the RECORD CONTAINS clause is explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
Although it is a part of the standard COBOL definition, the RECORD CONTAINS clause is explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program. 

