The Program-ID paragraph gives the name by which a program is identified and assigns selected program attributes to that program.
 The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a program prototype is identified.
The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a program prototype is identified.
 The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a call prototype is identified.
The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a call prototype is identified.
General Formats for Format 1
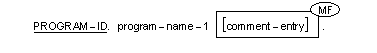
General Formats for Format 2

General Formats for Format 3



General Formats for Format 4

Directives
- In addition to Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify the reserved word list, the following directives may impact either the syntax or the semantics described in this section.
- CASE - determines whether upper-case and lower-case letters are considered equivalent.
- DEFAULT-BYTE - sets the value for data items defined in Working-Storage Section without a VALUE clause.
- MAPNAME - impacts the handling of non-alphabetic characters in the program-name.
- PROGID-COMMENT - causes Format 1 to be assumed rather than Format 2.
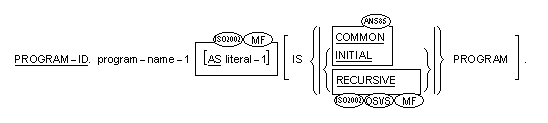
Syntax Rules for Formats1 and 2

 The first 8 characters of program-name-1 of a program that is not contained in another program should be unique in the system. The first character must be alphabetic; otherwise it is converted as follows:
The first 8 characters of program-name-1 of a program that is not contained in another program should be unique in the system. The first character must be alphabetic; otherwise it is converted as follows:
- 1 through 9 are changed to A through I respectively.
- Anything else is changed to J.
If a hyphen is used in characters 2 through 8 of program-name-1 in a program that is not contained in another program, it is changed to zero (0).
The MAPNAME Compiler directive controls this behavior.
 For programs that are contained in another program, program-name-1 can be any valid user-defined COBOL word, up to 30 characters long. The first eight characters need not be unique, and they will not be converted as described above. Lower-case letters are valid, but such program-names will be handled in a case-insensitive manner.
For programs that are contained in another program, program-name-1 can be any valid user-defined COBOL word, up to 30 characters long. The first eight characters need not be unique, and they will not be converted as described above. Lower-case letters are valid, but such program-names will be handled in a case-insensitive manner.
 A program contained within another program must not be assigned the same name as that of any other program contained within the compilation unit that contains this program.
A program contained within another program must not be assigned the same name as that of any other program contained within the compilation unit that contains this program.


Syntax Rules for Format 4

 Program-prototype-name-1 identifies the program prototoype. However, literal-1, if specified, is the name of the program prototype that is externalized to the operating environment.
Program-prototype-name-1 identifies the program prototoype. However, literal-1, if specified, is the name of the program prototype that is externalized to the operating environment.
General Rules for Formats 1 and 2
- Program-name-1 names the program declared by this program definition and is associated with the object code file pertaining to this program. Literal-1, if specified, is the name of the program that is externalized to the operating environment.

General Rules for Format 3
 Program-name-1 names the call prototype that will be used during syntax checking to determine the validity and nature of CALL literal statements.
Program-name-1 names the call prototype that will be used during syntax checking to determine the validity and nature of CALL literal statements.






![]()
![]() The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a program prototype is identified.
The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a program prototype is identified.
![]() The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a call prototype is identified.
The Program-ID paragraph specifies the name by which a call prototype is identified.
![]()
![]() Program-name-1 can be the same as another user-defined word.
Program-name-1 can be the same as another user-defined word.
![]() For programs that are contained in another program, program-name-1 can be any valid user-defined COBOL word, up to 30 characters long. The first eight characters need not be unique, and they will not be converted as described above. Lower-case letters are valid, but such program-names will be handled in a case-insensitive manner.
For programs that are contained in another program, program-name-1 can be any valid user-defined COBOL word, up to 30 characters long. The first eight characters need not be unique, and they will not be converted as described above. Lower-case letters are valid, but such program-names will be handled in a case-insensitive manner.
![]()
![]()
![]() or RECURSIVE
or RECURSIVE
![]()
![]() Any programs contained within a recursive program are recursive.
Any programs contained within a recursive program are recursive.
![]()
![]()
![]() A program in which the Local-Storage Section is specified is recursive.
A program in which the Local-Storage Section is specified is recursive.


